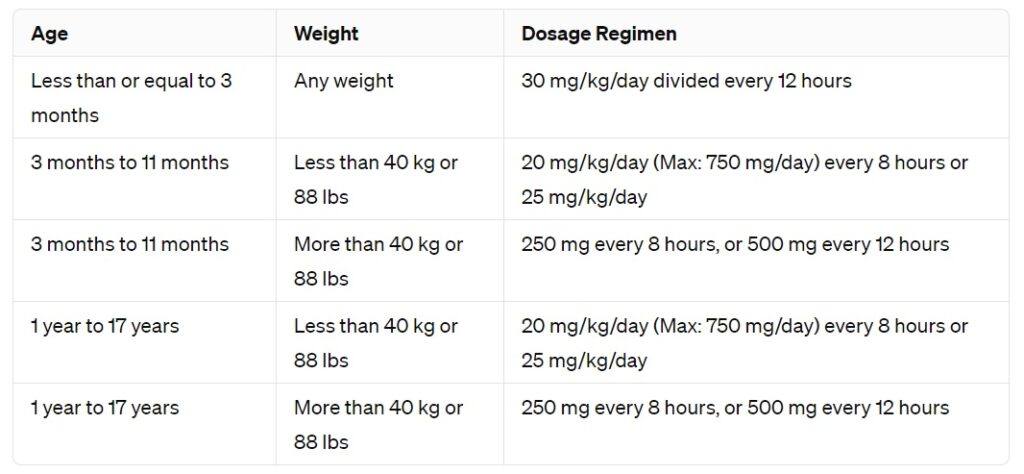
For children, accurate dosing of amoxicillin is critical in ensuring effective treatment while minimizing risks. The standard guideline suggests a dosage of 20-40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses, depending on the severity of the infection. For mild to moderate infections, 25 mg/kg/day is often sufficient, while more serious cases may require the upper limit.
Children weighing less than 10 kg typically receive a maximum of 250 mg per day, while those over 10 kg could have their dosage increased proportionately. It’s vital to adjust the dosage based on the child’s weight and the specific condition being treated. For instance, children with otitis media often require higher doses, around 45 mg/kg/day, to ensure effective eradication of the bacteria.
In cases of certain infections like pneumonia, higher doses of 90 mg/kg/day are recommended, emphasizing careful monitoring for any side effects. Always consult with a pediatrician for precise dosing tailored to a child’s health status, as individual needs may vary significantly based on age, weight, and underlying health issues.
- Amoxicillin Dosage Chart Pediatrics
- Understanding Amoxicillin for Children
- Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage Based on Age
- Calculating Dosage According to Body Weight
- Dosage Calculation Example
- Dosage Chart for Quick Reference
- Common Infections Treated with Amoxicillin in Pediatrics
- Key Considerations for Amoxicillin Administration
- Timing and Consistency
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Pediatric Dosage Adjustments for Special Conditions
- Adjustments for Obesity
- Dosing in Patients with Hepatic Dysfunction
- Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin in Children
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- When to Consult a Pediatrician About Dosage
Amoxicillin Dosage Chart Pediatrics
For pediatric patients, amoxicillin dosage often depends on the child’s weight and the condition being treated. The typical dosage is 20-40 mg/kg per day for most infections, divided into two or three doses. Here’s a simplified dosage chart:
Dosage by Weight:
- 10 kg (22 lbs): 200 mg daily (100 mg twice daily)
- 15 kg (33 lbs): 250 mg daily (125 mg twice daily)
- 20 kg (44 lbs): 400 mg daily (200 mg twice daily)
- 25 kg (55 lbs): 500 mg daily (250 mg twice daily)
- 30 kg (66 lbs): 600 mg daily (300 mg twice daily)
- 40 kg (88 lbs): 800 mg daily (400 mg twice daily)
For specific infections, the dosage may vary:
- Otitis Media: 80-90 mg/kg/day divided twice daily
- Pneumonia: 45 mg/kg/day divided twice daily
- Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 250 mg twice daily for 10 days
Always consult a pediatrician before administering amoxicillin to ensure proper dosage based on the child’s specific health needs. Adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment. Encourage liquid intake to aid absorption and reduce stomach upset.
Understanding Amoxicillin for Children
Amoxicillin is prescribed for various bacterial infections in children, including ear infections, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections. It’s a penicillin-type antibiotic that works effectively against a range of bacteria.
The dosage of Amoxicillin depends on the child’s age, weight, and the type of infection. Typically, doctors recommend:
- For children weighing less than 88 lbs (40 kg): 20 to 40 mg/kg/day divided into doses.
- For those weighing more than 88 lbs: the adult dosage of 500 mg to 875 mg per day may apply.
Administer the medication every 8 to 12 hours, depending on the prescription. Ensure consistent dosing to maintain the drug’s effectiveness in the body.
Possible side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Monitor your child for these symptoms and consult a healthcare provider if they occur.
Always complete the full course of Amoxicillin, even if symptoms improve, to prevent antibiotic resistance. Store Amoxicillin at room temperature, away from moisture and heat.
Check with a pediatrician before giving Amoxicillin, especially if your child has a history of allergies to penicillin or suffers from liver conditions. This ensures a safe and targeted treatment for your child’s specific needs.
Consult the prescribing information for the specific formulation (liquid, chewable, or tablet) to ensure correct administration. Liquid forms often require shaking before use to evenly distribute the medication.
If a dose is missed, administer it as soon as remembered unless it’s close to the next dose. Avoid doubling up to make up for a missed dose.
Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage Based on Age
For children aged 0 to 2 years, the typical dosage is 20 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. This approach ensures consistent medication levels throughout the day.
In children aged 2 to 12 years, recommend a dosage of 20-40 mg/kg/day, depending on the severity of the infection. For mild to moderate infections, aim for 20 mg/kg/day, while for more serious conditions, increase the dosage to 40 mg/kg/day.
For children over 12 years, the dosage can range from 500 mg to 875 mg daily, based on their weight and infection severity. Administer 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for more serious infections.
Always adjust dosages based on the child’s weight and the specific health professional’s guidance. Monitoring for any adverse reactions during treatment is essential.
Calculating Dosage According to Body Weight
For accurate dosage of Amoxicillin in pediatric patients, use the child’s body weight. The usual recommended dosage is 20-40 mg/kg per day, divided into two or three doses. For high severity infections, this can increase to 45 mg/kg/day. Always base your calculations on the child’s current weight in kilograms.
Dosage Calculation Example
For a child weighing 15 kg with a mild infection, calculate the dosage as follows:
Minimum dosage: 20 mg/kg x 15 kg = 300 mg per day.
Maximum dosage: 40 mg/kg x 15 kg = 600 mg per day.
Divide this total daily dosage into two or three doses. For 300 mg, administer 150 mg in two doses or 100 mg in three doses.
Dosage Chart for Quick Reference
| Weight (kg) | Min Dose (mg/day) | Max Dose (mg/day) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 200 | 400 |
| 15 | 300 | 600 |
| 20 | 400 | 800 |
| 25 | 500 | 1000 |
| 30 | 600 | 1200 |
Monitor the child’s response to treatment and adjust if necessary. Always consult a healthcare provider for specific advice tailored to individual cases.
Common Infections Treated with Amoxicillin in Pediatrics
Amoxicillin is frequently prescribed for respiratory tract infections in children, specifically otitis media (middle ear infections). Symptoms include ear pain and fever. A typical course involves 80-90 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses for 7 to 10 days.
Streptococcal pharyngitis, caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, is another common condition treated with this antibiotic. Children often present with sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Amoxicillin is dosed at 50 mg/kg/day for 10 days.
Amoxicillin effectively manages pneumonia in young patients, especially when the etiology is known to be bacterial. Treatment often involves 90 mg/kg/day for 7 to 10 days, particularly for community-acquired pneumonia.
In cases of skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis, Amoxicillin provides coverage against common bacteria. The recommended dosage is 50 mg/kg/day for 5 to 14 days, depending on severity.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children are also treated with Amoxicillin, particularly when caused by susceptible organisms. The usual dosage is 40 mg/kg/day for 7 to 10 days, ensuring effective resolution of symptoms.
This antibiotic plays an essential role in treating these infections, helping to alleviate symptoms and speed recovery in pediatric patients. Following the recommended dosages ensures optimal outcomes while minimizing the risk of resistance. Always consult a healthcare professional for specific guidance tailored to individual needs.
Key Considerations for Amoxicillin Administration
Administer amoxicillin only after confirming the child has a bacterial infection that is sensitive to this antibiotic. Always check for allergies, especially to penicillin. If there’s a history of allergic reactions, inform the healthcare provider immediately.
Dosage calculations depend on the child’s weight. The typical dosing for most infections ranges from 20 to 40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. Adjustments may be necessary in cases of renal impairment.
Timing and Consistency
For optimal absorption, administer amoxicillin at regular intervals. If your healthcare provider recommends three times daily dosing, choose consistent times to ensure steady medication levels in the bloodstream. Encourage compliance by linking doses to daily routines, such as meals.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Watch for common side effects, such as gastrointestinal upset, rash, or changes in behavior. Report any unusual symptoms to a healthcare provider. Maintain hydration and consider probiotic use to support gut health during and after antibiotic treatment.
Finally, complete the full course of the medication, even if symptoms improve before finishing the prescribed amount. Stopping early may lead to incomplete eradication of the bacteria.
Pediatric Dosage Adjustments for Special Conditions
For children with renal impairments, amoxicillin dosage must be adjusted based on the degree of dysfunction. The following guidelines provide insights for dosages based on creatinine clearance:
- Normal renal function (CrCl > 50 mL/min): Standard dosage applies.
- Mild impairment (CrCl 30-50 mL/min): Reduce the dose by 25%.
- Moderate impairment (CrCl 10-30 mL/min): Reduce the dose by 50%.
- Severe impairment (CrCl <10 mL/min): Consult a specialist; consider alternative therapies.
Adjustments for Obesity
In cases where a child is overweight, calculate the dose using their ideal body weight rather than actual weight. This adjustment helps avoid potential toxicity.
Dosing in Patients with Hepatic Dysfunction
While amoxicillin is primarily excreted by the kidneys, liver function should still be monitored. For children with significant liver impairment, consult pediatric infectious disease specialists to determine appropriate dosages.
For children with concurrent infections, dosages may need to be recalibrated, especially if antibiotic resistance is a concern. Regular assessment of symptoms and response to treatment guides any necessary modifications.
Always reevaluate the child’s condition during treatment to ensure optimal outcomes. Close collaboration with healthcare providers enhances safety and efficacy in managing complex cases.
Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin in Children
Administering amoxicillin to children can lead to various side effects. Awareness of these potential reactions aids in prompt intervention. Regular monitoring of your child’s response to the medication is advisable.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some children may experience gastrointestinal upset, including nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea: Loose stools can occur; it’s essential to maintain hydration during this time.
- Rash: Skin rashes may develop as a reaction; notify a healthcare provider if this occurs.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms may include swelling, difficulty breathing, or severe rash. Seek immediate medical assistance if these occur.
- Clostridium difficile Infection: This infection can cause severe diarrhea and requires specific treatment. Be vigilant for symptoms.
- Liver Issues: Look for signs of jaundice, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, which may indicate liver stress.
Always consult with a healthcare professional if any concerning symptoms arise. Ensuring your child’s safety while taking amoxicillin is crucial for effective treatment.
When to Consult a Pediatrician About Dosage
Consult a pediatrician if your child is under two years old and requires amoxicillin. Their dosage often depends on weight and specific health conditions, and a healthcare professional can provide accurate adjustments.
If your child has been prescribed amoxicillin but displays unusual symptoms, such as persistent vomiting, diarrhea, or skin rash, seek advice immediately. Such reactions may indicate an allergic response or side effects that require attention.
Pay attention to any fever that persists after 48 hours of treatment with amoxicillin. This could signal an underlying infection or the necessity to change the antibiotic. Contact your pediatrician for further evaluation.
Monitor your child’s weight regularly. If there’s a significant weight change, or if they are experiencing growth concerns, discuss dosage adjustments with your pediatrician. Accurate dosages often depend on proper weight assessments.
If your child has a history of kidney issues, inform your pediatrician before starting amoxicillin. Special dosage considerations may be necessary, and only a healthcare provider can recommend the appropriate course of action.
| Reason for Consultation | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Child under 2 years | Consult pediatrician before dosage |
| Unusual symptoms | Seek immediate advice |
| Fever persists after 48 hours | Contact pediatrician |
| Significant weight change | Discuss dosage adjustment |
| History of kidney issues | Inform pediatrician before treatment |
Always keep lines of communication open with your pediatrician about any concerns or changes in your child’s health while on amoxicillin. Their guidance ensures that your child receives the safest and most effective treatment.