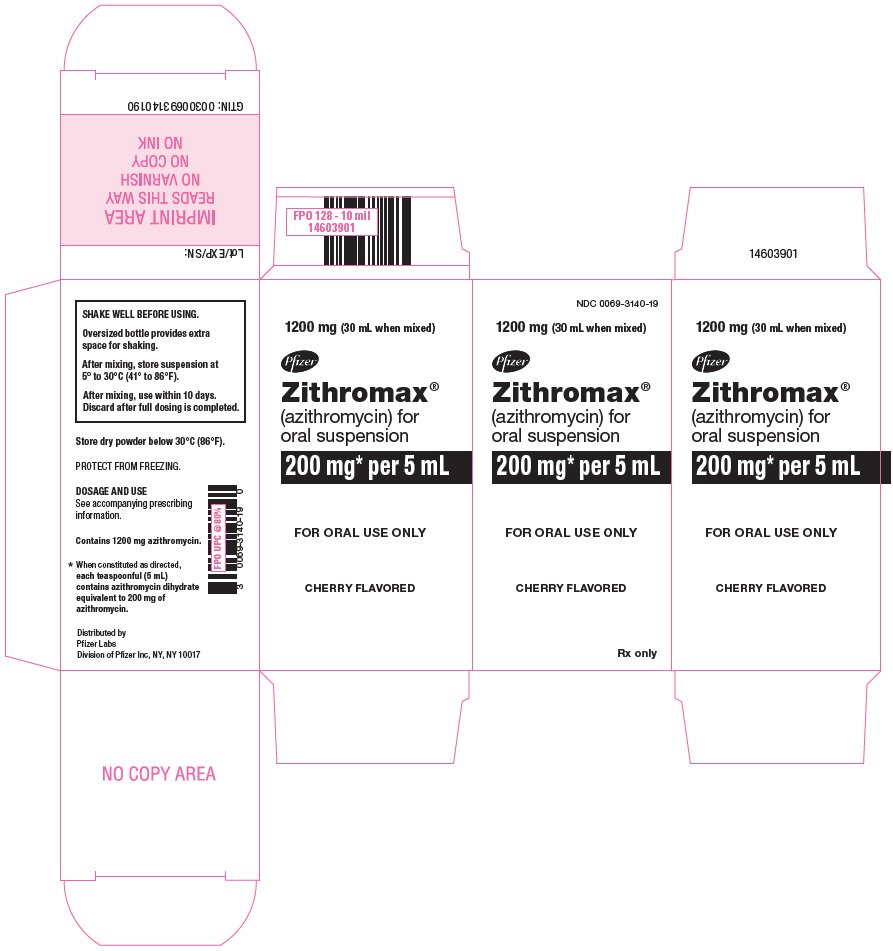
The Azithromycin package insert from Pfizer provides critical information for healthcare professionals and patients. It details indications, dosage, and important safety data. Patients should familiarize themselves with this insert to understand the medication’s purpose and proper use.
Azithromycin is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections and skin infections. The typical adult dosage ranges from 500 mg to 2000 mg, depending on the type of infection being treated. Adherence to these dosing guidelines is essential for the treatment’s success.
Side effects can occur, ranging from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to more serious allergic reactions. Monitoring patient responses to the medication can help identify any adverse effects early. This insert emphasizes the importance of informing patients about these potential reactions and the need for immediate medical attention if they arise.
Interactions with other medications are highlighted in the insert, advising healthcare providers to review patients’ current medications to prevent adverse effects. This practice ensures a safer treatment approach for individuals taking Azithromycin.
Lastly, the insert includes storage recommendations, advising that the medication be kept away from moisture and heat to maintain its efficacy. Proper storage contributes to the medication’s overall effectiveness, ensuring that patients receive the full benefits of their prescribed treatment.
- Azithromycin Package Insert Pfizer
- Overview of Azithromycin
- Indications
- Dosing and Administration
- Indications for Use
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Adult Dosage
- Pediatric Dosage
- Mechanism of Action of Azithromycin
- Key Aspects of Azithromycin’s Mechanism
- Pharmacokinetics and Distribution
- Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Serious Adverse Reactions
- Monitoring and Management
- Drug Interactions to Consider
- Warnings and Precautions for Patients
- Cardiac Considerations
- Allergic Reactions
- Storage and Handling Instructions
- Frequently Asked Questions About Azithromycin
- What are the common side effects of Azithromycin?
- Can I take Azithromycin with other medications?
Azithromycin Package Insert Pfizer
Azithromycin is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections including respiratory, skin, and sexually transmitted infections. Dosage and administration depend on the specific condition being treated. For acute bacterial sinusitis, a typical regimen is 500 mg on the first day followed by 250 mg daily for four additional days.
Patients should take azithromycin with or without food, but consistent timing is recommended. Ensure a full course of therapy is completed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps prevent bacterial resistance.
Monitor for signs of hepatotoxicity, especially in patients with liver disease or those taking medications that impact liver function. If severe allergic reactions occur, discontinue the use of azithromycin immediately.
Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Administration in infants and children requires careful dosing adjustments to avoid potential toxicities.
Drug interactions may occur with medications like warfarin, leading to increased bleeding risk. Always disclose current medications to healthcare providers prior to starting treatment.
Consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen during treatment. Regular follow-ups may be necessary to assess the resolution of the infection and manage any adverse effects.
Overview of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is an antibiotic used primarily to treat various bacterial infections. It falls under the macrolide class and works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, ultimately stopping their growth. This medication is prescribed for respiratory tract infections, skin infections, ear infections, and sexually transmitted diseases, among others.
Indications
Doctors commonly recommend azithromycin for infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis, and infections caused by specific bacteria like Chlamydia and Mycoplasma. Its ability to penetrate tissues allows it to reach high concentrations in infected areas, leading to positive treatment outcomes.
Dosing and Administration
Azithromycin is typically administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection. A common regimen starts with a loading dose, followed by daily doses for a specified duration. Adhering strictly to the prescribed course is crucial for effectiveness and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Indications for Use
Azithromycin is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections. Utilize this antibiotic for respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis, when caused by susceptible organisms. It effectively addresses skin and soft tissue infections, as well as certain sexually transmitted infections.
In cases of acute bacterial sinusitis, consider azithromycin as a treatment option, especially in patients who have a penicillin allergy. For patients diagnosed with otitis media, azithromycin offers a reliable alternative.
This medication also serves as prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis in at-risk individuals undergoing dental procedures. Lastly, azithromycin is indicated in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia caused by specific pathogens.
Ensure proper diagnostics to guide the choice of azithromycin, confirming the presence of bacterial infections and susceptibility to this antibiotic. Always consult healthcare professionals for appropriate use based on individual patient circumstances.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Azythromycin is commonly prescribed based on the specific condition being treated. Follow these dosage recommendations for optimal results.
Adult Dosage
- For respiratory infections, administer 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg daily for four days.
- For skin infections, provide a total of 1,500 mg over three days: 500 mg on day one, followed by 250 mg on days two and three.
- For sexually transmitted infections (e.g., chlamydia), a single dose of 1,000 mg is recommended.
Pediatric Dosage
- The recommended dosage for children aged 6 months to 12 years is 10 mg/kg on the first day, then 5 mg/kg daily for the next four days.
- For children over 12 years, follow the adult dosing guidelines as appropriate.
Administer Azithromycin at least one hour before or two hours after meals to ensure optimal absorption. Liquid formulations should be shaken well before use. Monitor patient response and adjust dosage as necessary, especially for those with kidney or liver impairments.
Mechanism of Action of Azithromycin
Azithromycin acts primarily by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, which is vital for bacterial growth and reproduction. It binds to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, blocking the peptide transferase activity and preventing the elongation of the peptide chain.
Key Aspects of Azithromycin’s Mechanism
- Targeting Ribosomes: Azithromycin specifically targets the 23S rRNA component of the 50S ribosomal subunit, interfering with the normal function of the ribosome.
- Inhibition of Translation: By blocking the peptidyl transferase center, azithromycin halts translation, effectively stopping the production of proteins that bacteria need to survive.
- Bacteriostatic Effect: While it is bacteriostatic against many organisms, in higher concentrations, it can exhibit bactericidal properties.
Pharmacokinetics and Distribution
Azithromycin has a unique pharmacokinetic profile. After oral administration, it achieves high tissue concentrations, particularly in the lungs, skin, and soft tissues. This allows for prolonged antibacterial activity even after the drug has been cleared from the bloodstream.
- Half-Life: Azithromycin has a half-life of approximately 68 hours, enabling once-daily dosing.
- Tissue Accumulation: The drug accumulates in tissues and is slowly released, providing a sustained antibacterial effect.
Understanding these mechanisms helps in optimizing the use of azithromycin for treating various bacterial infections while anticipating potential resistance patterns in clinical settings.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Patients using Azithromycin may experience various side effects. Common reactions include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms often resolve after a short period; however, if they persist, consult your healthcare provider.
Serious Adverse Reactions
Serious side effects require immediate medical attention. These include severe allergic reactions characterized by rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. Cardiac effects, such as irregular heartbeats, may also occur, particularly in individuals with a history of heart conditions. Monitor for any signs of liver problems, including yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, and persistent abdominal pain.
Monitoring and Management
Regular check-ups can help assess any potential side effects during treatment. Always inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are currently taking to avoid interactions that could exacerbate side effects. If experiencing unusual or severe symptoms, discontinue use and seek medical advice promptly.
Drug Interactions to Consider
Monitor interactions between azithromycin and anticoagulants, particularly warfarin. Azithromycin can enhance the anticoagulant effects, increasing bleeding risk. Regularly check INR levels to ensure safe dosing.
Assess the use of azithromycin in conjunction with other medications that prolong QT interval, such as certain antiarrhythmics (e.g., quinidine, procainamide). The combination may heighten the risk of arrhythmias. Continuous ECG monitoring is advisable.
Be cautious with antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, as they can reduce the absorption of azithromycin. Administer these antacids at least two hours before or after azithromycin to maintain its effectiveness.
Evaluate the compatibility of azithromycin with statins. Some patients may experience increased statin levels, leading to a higher likelihood of liver toxicity. Monitor liver function tests if both medications are prescribed.
If a patient is on cyclosporine, adjust the dosage carefully. Azithromycin may raise cyclosporine levels, necessitating more frequent monitoring of drug levels to avoid toxicity.
Discuss with patients the potential interactions with medications for seizure disorders. Azithromycin may affect the metabolism of certain anticonvulsants, increasing the risk of seizures. Maintain regular follow-ups to adjust anticonvulsant dosages if needed.
Warnings and Precautions for Patients
Patients taking Azithromycin should be aware of potential risks. Inform healthcare providers about all medications and supplements to avoid interactions. Caution is advised for individuals with a history of liver disease, kidney problems, or arrhythmias.
Cardiac Considerations
Azithromycin has been associated with QT prolongation, which can lead to serious heart rhythm abnormalities. Patients with existing heart conditions, particularly those on drugs affecting heart rhythm, should undergo regular monitoring.
Allergic Reactions
Watch for signs of an allergic reaction, such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. If any of these symptoms occur, seek medical attention immediately. Patients with a known allergy to macrolide antibiotics should not use Azithromycin.
Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals need to discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before starting treatment. Maintaining communication with your healthcare team ensures the safe use of Azithromycin while managing any underlying health issues effectively.
Storage and Handling Instructions
Store Azithromycin at a controlled room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect the medication from light and moisture. Keep it in its original packaging until use to maintain its stability.
Ensure that the product is out of reach of children and pets. Do not place it in areas prone to temperature fluctuations, such as bathrooms or near windows. Avoid freezing; if exposed to low temperatures, the effectiveness may be compromised.
Inspect the packaging for any signs of damage or tampering before use. If you notice any alterations, consult your pharmacist for further guidance. Dispose of any unused medication responsibly–do not flush it down the toilet or pour it down the drain.
| Storage Condition | Recommended Temperature | Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temperature | 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) | Protect from light and moisture |
| Freezing | Avoid | – |
| Child Safety | Keep out of reach | – |
For any specific inquiries regarding storage beyond the provided instructions, contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Follow local regulations for the disposal of pharmaceutical products to ensure safety and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Azithromycin
For patients prescribed Azithromycin, it is crucial to follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider. Typically, a common regimen for treating respiratory infections involves taking the medication for five days, but specifics can vary based on the infection’s nature.
What are the common side effects of Azithromycin?
Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Some individuals may experience headaches or dizziness. If these effects persist or worsen, consult your doctor for advice.
Can I take Azithromycin with other medications?
Azithromycin may interact with certain medications, including anticoagulants and medications for arrhythmia. Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you currently take to avoid potential interactions.