Use Lasix as prescribed, typically once or twice daily, to manage fluid retention and hypertension. Monitor your daily weight to track fluid loss and report any sudden changes to your healthcare provider. This practice helps ensure the medication is working effectively.
Stay hydrated while taking Lasix, but be mindful of your fluid intake as advised by your doctor. It’s essential to find the right balance since excessive dehydration can lead to complications. Carry water with you and sip throughout the day, especially during hot weather or physical activity.
Be aware of potential side effects. Common reactions include dizziness, lightheadedness, and increased urination. If you experience severe side effects like a rapid heartbeat or unusual confusion, contact your healthcare professional immediately.
Schedule regular check-ups to monitor kidney function and electrolyte levels. Lasix can affect potassium levels, so your doctor may recommend potassium-rich foods such as bananas, oranges, or spinach, or prescribe a potassium supplement if needed.
Educate yourself about the signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, excessive thirst, or decreased urination. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for timely intervention, helping maintain your health while on Lasix.
Patient Teaching for Lasix
Take Lasix exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Monitor your dosage and timing diligently to maintain consistent levels in your system.
Stay hydrated, but balance your fluid intake as advised, especially if you’re experiencing increased urination. Drinking too much or too little can impact your treatment.
Watch for signs of dehydration such as dry mouth, dizziness, or excessive thirst. Contact your provider if you notice any of these symptoms.
Regularly check your weight, ideally at the same time each day. Sudden weight changes could indicate fluid retention or loss, signaling the need for dosage adjustments.
Keep an eye on your blood pressure, as Lasix can affect it. Report any significant changes to your healthcare provider promptly.
Schedule routine blood tests to monitor electrolytes, especially potassium levels. Consuming potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach can help maintain electrolyte balance.
- Limit salt intake, as it can counteract the effects of Lasix.
- Avoid over-the-counter medications that may contain sodium.
- Be cautious with supplements or herbal remedies. Discuss them with your doctor beforehand.
Inform any healthcare professional involved in your care about your Lasix usage, especially before surgery or new medications.
Plan rests during the day, particularly if you feel lightheaded or tired. Taking it slow can help you manage any side effects.
Report side effects such as rash, muscle cramps, or irregular heartbeat to your healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent complications.
Educate yourself about the purpose of Lasix. Understanding how it works can help reinforce the importance of sticking to your treatment plan.
Understanding the Purpose and Indications of Lasix
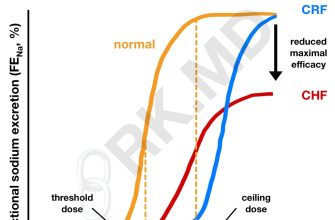
Lasix, or furosemide, serves primarily as a diuretic, helping to reduce fluid retention in the body. Patients commonly use it to manage conditions like heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and kidney disorders. By promoting the excretion of sodium and water, Lasix decreases blood pressure and alleviates symptoms related to fluid overload, such as swelling and shortness of breath.
Common Indications
Doctors prescribe Lasix for various reasons. It effectively treats hypertension, especially when other medications are insufficient. Additionally, Lasix plays a critical role in acute pulmonary edema, providing relief by reducing excess fluid in the lungs. Patients with conditions such as renal disease also benefit, as it helps manage electrolyte imbalances and fluid retention.
Administration and Dosage
Lasix is usually administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition. Healthcare providers adjust the dosage based on individual needs, often starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it. Regular monitoring of kidney function and electrolytes is essential to prevent potential side effects and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Recognizing Potential Side Effects and When to Seek Help
Monitor for signs of dehydration such as excessive thirst, dry mouth, or decreased urine output. Lasix (furosemide) can lead to electrolyte imbalances, so watch for symptoms like muscle cramping, weakness, or fatigue.
Be alert for sudden changes in weight. Rapid weight gain or loss may indicate fluid retention or excessive diuresis. If you notice a gain of more than 2-3 pounds in a day, contact your healthcare provider.
Recognize the importance of monitoring blood pressure. Lasix can cause low blood pressure, which may present as dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly upon standing. Report these feelings to your doctor, especially if they are severe or persistent.
Pay attention to signs of allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives. Seek immediate medical assistance if you experience these symptoms.
Keep an eye out for changes in hearing or balance, as high doses of Lasix may affect these senses. If you notice ringing in the ears or any hearing changes, inform your healthcare provider promptly.
Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor kidney function and electrolyte levels. Ensure you attend all scheduled appointments and discuss any fluctuations in your results with your doctor.
If you experience persistent nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, reach out to your healthcare provider. These may indicate adverse reactions to the medication or complications from fluid loss.
In cases of severe abdominal pain or gastrointestinal distress, seek medical attention promptly, as this could indicate a more serious issue.
Guidelines for Proper Administration and Monitoring
Administer Lasix (furosemide) intravenously or orally as prescribed. For intravenous use, infuse slowly over at least 1-2 minutes to minimize the risk of ototoxicity. Adjust the dose based on the patient’s response, renal function, and the specific condition being treated.
Monitoring Fluid and Electrolytes
Regularly assess renal function by checking creatinine and electrolyte levels. Monitor for signs of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, particularly hypokalemia. Encourage patients to report symptoms such as muscle cramps, weakness, or irregular heartbeats.
Assessing Patient Outcomes
Evaluate the effectiveness of Lasix by monitoring weight, urine output, and blood pressure. Document any changes in edema and overall fluid status. Schedule follow-up appointments to reassess dosage adjustments and ongoing treatment needs.