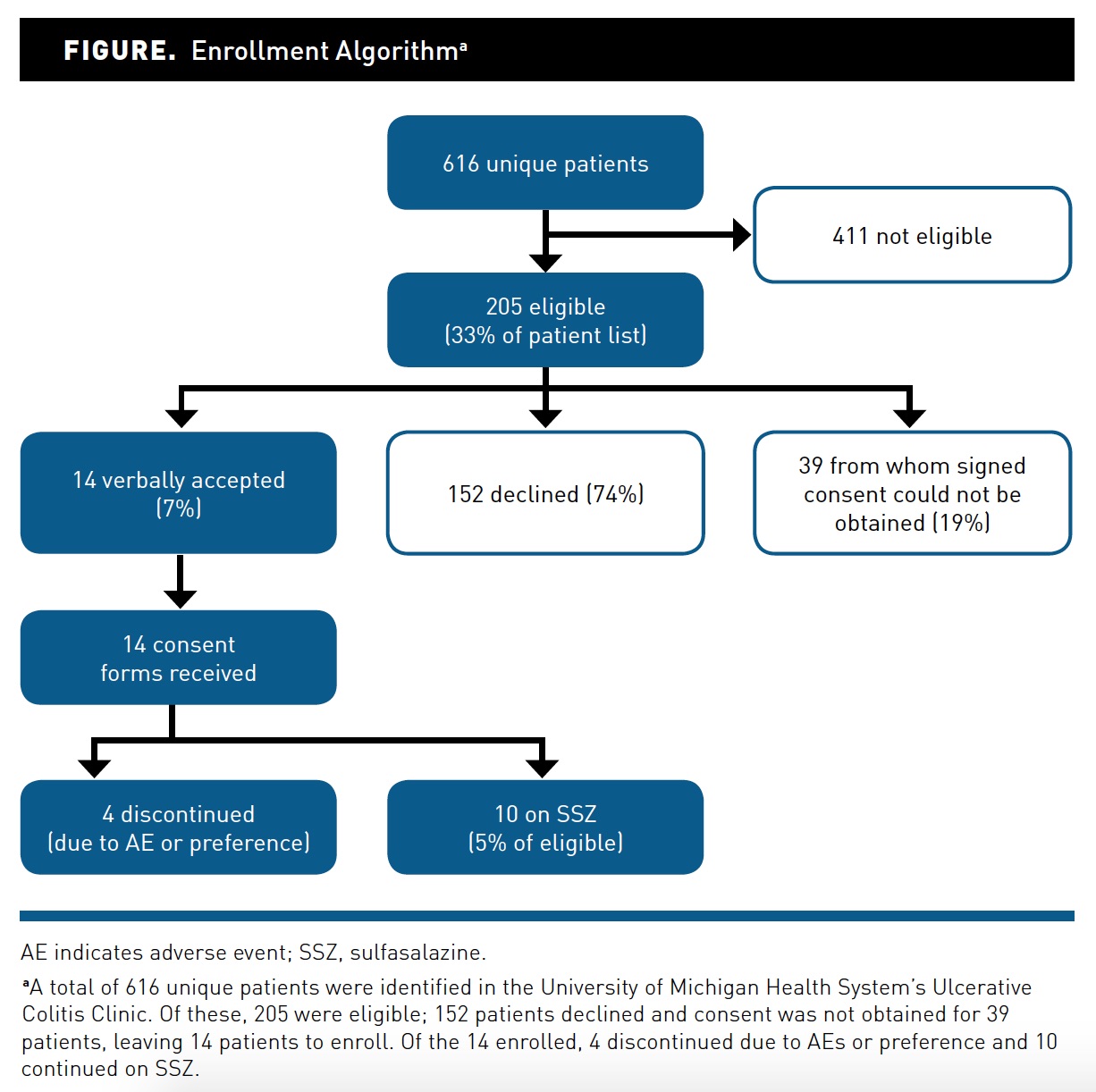
The recommended starting dose of sulfasalazine for adults with ulcerative colitis is typically 2 to 4 grams per day, divided into two or three doses. Adjustments can be made based on individual response and tolerability. For those starting treatment, it is advisable to begin at the lower end of the dosing range and gradually increase to minimize potential side effects.
After initiating treatment, monitor the patient’s response closely. If symptoms improve, a maintenance dose of 2 grams per day may be sufficient for long-term management. However, in cases where symptoms persist or flare-ups occur, doses can be increased, with a maximum daily dose of up to 6 grams typically considered safe under supervision.
Regular follow-ups and laboratory tests are recommended to assess efficacy and monitor for possible adverse effects, such as liver function impairment or hematological abnormalities. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals with renal or liver issues. Always consult with a healthcare professional before altering any treatment regimen.
- Sulfasalazine Dose for Ulcerative Colitis
- Recommended Dosages for Adult Patients
- Adjustments and Maintenance
- Administration Tips
- Adjustments for Pediatric Patients
- Gradual Dose Escalation
- Monitoring and Safety
- Titration of Sulfasalazine Dose
- Monitoring and Managing Side Effects
- Clinical Guidelines and Recommendations
Sulfasalazine Dose for Ulcerative Colitis
The standard initial dose of sulfasalazine is 2 to 4 grams per day, divided into multiple doses. Patients typically start with a lower dose of 500 mg to 1 gram twice daily, which can be gradually increased based on tolerance and response.
For maintenance therapy, the dose may range from 2 to 4 grams per day, depending on the severity of the condition and clinical response. Regular monitoring is essential to adjust the dosage and to manage any potential side effects.
Follow these guidelines for dosage adjustments:
- Increase the dose by 500 mg to 1 gram every week, until the desired effect is achieved.
- Consult with a healthcare provider if side effects occur, such as nausea, headache, or rash.
- Monitor blood counts regularly due to the risk of hematological side effects.
Hydration is important while taking sulfasalazine. Encourage adequate fluid intake to prevent renal impairment.
In specific cases, such as pregnancy or existing medical conditions, discuss any modifications of the dosage with a healthcare professional. Each patient’s situation is unique, and tailored treatment plans are often necessary.
Recommended Dosages for Adult Patients
The typical starting dosage of sulfasalazine for adults with ulcerative colitis is 500 mg taken orally four times a day. This can be increased gradually based on the patient’s response and tolerance, with a common target dose of 2 to 4 grams per day, divided into multiple doses.
Adjustments and Maintenance
After achieving an optimal response, maintenance therapy often involves a dosage of 1.5 to 3 grams daily. Adjustments may be necessary based on clinical response and any side effects experienced by the patient.
Administration Tips
Take the medication with food to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Drinking plenty of fluids helps prevent dehydration and urinary issues associated with sulfasalazine use.
Regular monitoring of blood counts and liver function is recommended during treatment to detect potential adverse effects early. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and adjustments specific to individual health needs.
Adjustments for Pediatric Patients
The recommended sulfasalazine dose for pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis is typically based on body weight. Begin with an initial dose of 30 mg/kg/day, divided into two to three doses. For children, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. Monitoring for efficacy and side effects is crucial, especially during dose adjustments.
Gradual Dose Escalation
Start with a lower dose and increase gradually. This approach minimizes side effects and allows the child to adjust to the medication. After two to four weeks, consider increasing the dose by 5 mg/kg every week until the desired response is achieved, keeping within the maximum allowable limit.
Monitoring and Safety
Regular follow-ups are essential. Monitor for common side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and rashes. Hematological parameters should be checked periodically to detect possible leukopenia or thrombocytopenia. Adjust the dosing schedule as needed based on the child’s response and any adverse reactions.
Titration of Sulfasalazine Dose
Start with an initial dose of 500 mg of sulfasalazine twice daily. Assess tolerance over the first week. If the patient tolerates this dose well, increase it to 1,000 mg twice daily after seven days.
Continue titrating the dose upwards by 500 mg increments every week. The usual maximum daily dose reaches 3,000 mg, divided into two or three doses. Monitor for side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbance and headache, during each incremental increase.
Evaluate the patient’s response to treatment regularly. Adjust the dose based on clinical effectiveness and tolerability. In cases of inadequate response or side effects, reducing the dose or discontinuing therapy may be necessary.
Always consider renal function, as dosage adjustments may be required for patients with impaired renal status. Regular blood tests can help monitor potential adverse effects, including changes in blood counts and liver function. This proactive approach maximizes benefits while minimizing risks during treatment for ulcerative colitis.
Monitoring and Managing Side Effects
Regular monitoring for side effects when using sulfasalazine for ulcerative colitis is key to maintaining health and optimizing treatment outcomes. Be proactive and communicate any changes to your healthcare provider promptly.
Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Rash
- Fatigue
Implement the following strategies to manage side effects effectively:
- Daily symptom checklist: Maintain a daily log of any side effects experienced, noting severity and duration. This information will aid discussions with healthcare providers.
- Adjusting dosage: Consult your doctor about adjusting the sulfasalazine dose if side effects become pronounced. A gradual dose escalation can sometimes mitigate discomfort.
- Hydration: Increase fluid intake to help reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Staying hydrated also supports overall health.
- Diet modifications: Incorporate bland foods if nausea occurs. Avoid triggers like spicy, fatty, or fried items.
- Regular blood tests: Schedule routine blood tests as recommended by your doctor to monitor liver function and blood cell counts, assessing for rare but serious side effects.
- Sunscreen: Apply sunscreen frequently since sulfasalazine can increase sensitivity to sunlight, minimizing the risk of sunburn.
- Support resources: Consider joining support groups where you can share experiences and coping strategies with others on the same medication.
Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication or lifestyle. Your well-being is the priority, and tailored strategies can enhance comfort during treatment.
Clinical Guidelines and Recommendations
The standard starting dose of sulfasalazine for adults with ulcerative colitis is typically 2 grams per day, administered in two to four divided doses. This can be adjusted based on individual patient response and tolerance.
For maintenance therapy, the dosage may range between 1 to 2 grams daily. Some patients may benefit from higher doses, particularly during active disease phases. Regular monitoring for side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or hypersensitivity reactions, is suggested.
Table 1 outlines the recommended dosing regimen based on the severity of ulcerative colitis:
| Condition Severity | Initial Dose | Maintenance Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 2 g/day | 1 g/day |
| Moderate | 2-4 g/day | 2 g/day |
| Severe | 4 g/day | 2-4 g/day |
Patients should be counseled on potential side effects, including nausea, headache, and skin rashes. Routine laboratory tests, such as complete blood count and liver function tests, are advisable every 2-4 weeks during the initial therapy phase and at intervals thereafter.
In cases where sulfasalazine is not tolerated or effective, alternative therapies such as mesalamine or corticosteroids should be considered. Personalized treatment plans remain crucial for optimal management of ulcerative colitis.